Content
Retained Earnings is Beginning Retained Earnings + Revenue – Expenses – Dividends – Stock Repurchases. Because the Alphabet, Inc. calculation shows that the basic accounting equation is in balance, it’s correct. And the double-entry accounting system is working. A screenshot of Alphabet Inc Consolidated Balance Sheets from its 10-K annual report filing with the SEC for the year ended December 31, 2021, follows.
- This transaction affects only the assets of the equation; therefore there is no corresponding effect in liabilities or shareholder’s equity on the right side of the equation.
- Essentially, the representation equates all uses of capital to all sources of capital, where debt capital leads to liabilities and equity capital leads to shareholders’ equity.
- In the chart of accounts, the balance sheet accounts are normally listed in which order?
- So it will result in a decrease in assets and liabilities.
- The effects of changes in the items of the equation can be shown by the use of + or – signs placed against the affected items.
In a corporation, capital represents the stockholders’ equity. Thus, the accounting formula essentially shows that what the firm owns has been purchased with equity and/or liabilities. Current assets include cash and cash equivalents, accounts the basic accounting equation may be expressed as receivable, inventory, and prepaid assets. Current liabilities are short-term financial obligations payable in cash within a year. Current liabilities include accounts payable, accrued expenses, and the short-term portion of debt.
What Is the Accounting Equation and Why Does It Matter?
Its applications in accountancy and economics are thus diverse. Regardless of how the accounting equation is represented, it is important to remember that the equation must always balance. On 31 January, the electricity bill of $500 is paid. This transaction would decrease cash and owner’s equity. The difference between the sale price and the cost of merchandise is the profit of the business that would increase the owner’s equity by $1,000 (6,000 – $5,000).
- There is no effect on the total amount of assets.
- Billie Nordmeyer works as a consultant advising small businesses and Fortune 500 companies on performance improvement initiatives, as well as SAP software selection and implementation.
- Leases can’t make it on this list because they’re not technically owned by the company.
- This article gives a definition of accounting equation and explains double-entry bookkeeping.
The only equity is Sam’s capital (i.e., owner’s equity amounting to $100,000). The properties owned by a business are called assets. The rights or claims to the properties are referred to as equities. Is a list of accounts with their balances at a given time. Pay additional dividends, acquire property, plant and equipment, and pay off debts.
Exercises For Accounting Equation
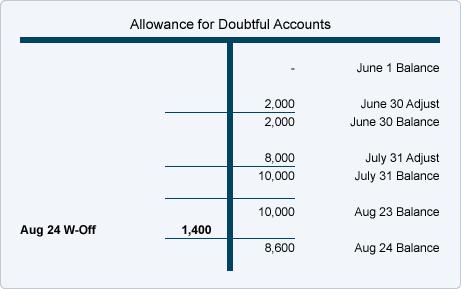
A debit refers to an increase in an asset or a decrease in a liability or shareholders’ equity. A credit in contrast refers to a decrease in an asset or an increase in a liability or shareholders’ equity. One of the main benefits of using the accounting equation is the fact that it provides an easy way to verify the accuracy of your bookkeeping. It also helps measure the profitability of your business. Are your liabilities significantly higher than your assets? This may indicate that you aren’t managing your money very well.
A mark in the debit column will increase a company’s asset and expense accounts, but decrease its liability, income, and capital account. For example, assume a company purchases office supplies on credit for $6 thousand and a credit is entered to the vendor payable account. A month later the company receives the vendor’s invoice and immediately pays the invoice amount in full. The payment leads to a $6,000 credit entry to the cash account and a $6,000 debit entry to the vendor payable account.
The accounting equation may be expressed as – The…
For your ease let’s assume that equity is the difference between assets and liabilities or it is the money that you have introduced and retained from business profit. To ensure that a company is “in balance,” its assets must always equal its liabilities plus its owners’ equity. Equity is named Owner’s Equity, Shareholders’ Equity, or Stockholders’ Equity on the balance sheet. Business owners with a sole proprietorship and small businesses that aren’t corporations use Owner’s Equity. Corporations with shareholders may call Equity either Shareholders’ Equity or Stockholders’ Equity.


